Lithium batteries are expensive due to high raw material costs, complex manufacturing, R&D investments, and environmental and ethical challenges.
Introduction
Lithium batteries, powering a vast range of devices from smartphones to electric vehicles, are undeniably central to our modern lives. The journey of these batteries from their invention to their current status is both intriguing and complex. When diving deeper into the subject, we often find ourselves asking, “Why are these batteries so expensive?”
Brief Overview of Lithium Batteries
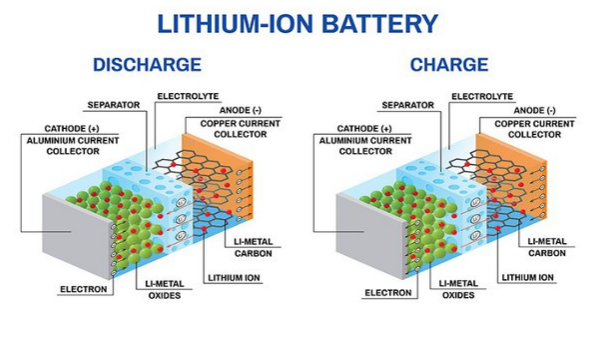
Lithium batteries are a type of rechargeable battery where lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharging, and vice versa when charging. They are known for their high energy density, which means they can store a significant amount of energy in a relatively small space. This has made them particularly favorable for portable electronics, such as smartphones and laptops. They’re also crucial in larger applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
Importance in Modern Technology
In the past decade, the demand for lithium batteries has skyrocketed, primarily due to the growth of the electric vehicle market. As of 2020, it was estimated that around 3% of global car sales were electric. With major automakers announcing their plans to phase out internal combustion engines in the coming years, this percentage is projected to rise significantly.
Historical Context
The origin and progression of lithium batteries offer valuable insights into their current price structure. By tracing back their development, one can begin to comprehend the challenges and milestones that have shaped their present status.
Development of Lithium Batteries
The conception of lithium batteries began in the 1970s when researchers commenced experimentation with lithium as a battery material due to its exceptional electrochemical potential. By the 1980s, the first non-rechargeable lithium batteries appeared in the market. Yet, their volatile nature restricted widespread use.
A breakthrough came in 1991 when Sony and Asahi Kasei released the first commercial rechargeable lithium-ion battery. The innovation relied on lithium cobalt oxide, a stable compound that drastically reduced the risks previously associated with lithium batteries. This pioneering battery technology opened doors for numerous applications, especially in the realm of portable electronics.
Evolution of Battery Prices
While lithium-ion batteries started as a costly technology, prices have steadily decreased over the years, thanks to economies of scale, technological advancements, and increased competition in the market.
Raw Materials and Production
The production process and the raw materials used in lithium-ion batteries play a vital role in determining their cost. From acquiring these materials to transforming them into functional batteries, each step incurs expenses that cumulatively shape the final price.
Key Materials Used
The primary components of a lithium-ion battery are the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separators. Each of these components demands specific materials that influence the battery’s efficiency, durability, and cost.
Lithium Sources and Extraction
Lithium, the primary material, usually comes from two main sources: hard rock mines and brine deposits. While Australia leads the world in hard rock mining, countries like Chile dominate in brine extraction from salt flats. Extracting lithium from these sources is energy-intensive and requires significant water resources, especially for brine deposits. As demand for lithium rises, the cost of extraction also increases. For instance, the price of lithium carbonate, an essential form used in batteries, surged from $7,474 per ton in 2015 to over $12,000 per ton in 2018, reflecting the pressure on supply chains.
Cobalt and Nickel Mining
Cobalt and nickel are critical for producing the cathodes of many lithium-ion batteries. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) produces over 60% of the world’s cobalt. The concentration of these resources in specific geographical regions and the concerns about ethical mining have pushed the prices. For instance, cobalt prices spiked from under $15/lb in 2016 to over $40/lb in 2018.
Production Challenges
Creating a lithium-ion battery isn’t just about procuring raw materials. The manufacturing process is intricate, with several challenges contributing to the costs.
Complex Manufacturing Processes
The process of producing a lithium-ion battery involves various stages, from electrode preparation and cell assembly to formation cycling. Ensuring consistency and high-quality output demands precision and advanced machinery. As technology has advanced, batteries have become more intricate, demanding higher purity materials and more delicate manufacturing processes, which contribute to higher costs.
Quality Control and Safety Measures
Given the energetic nature of lithium-ion batteries, ensuring they are safe for consumer use is paramount. Manufacturers must invest in quality control measures to prevent any defects that might cause battery failures or fires. Safety tests, including overcharge, short-circuit, and puncture tests, are mandatory before releasing batteries to the market. Such rigorous quality checks and the associated equipment add to the production costs.
Understanding these complexities provides a clearer picture of why producing high-quality, reliable lithium-ion batteries remains an expensive endeavor.
Demand and Supply Dynamics
A primary factor influencing the price of any product, lithium-ion batteries included, is the dynamic interplay between demand and supply. As our world grows increasingly electrified, understanding these dynamics provides crucial insights into battery price trends.
Growing Demand for Electric Vehicles
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a major driver for increasing lithium-ion battery demand. Governments worldwide are pushing for greener transportation solutions to combat climate change, resulting in policies that favor EVs. For instance, in 2019, EVs represented 2.5% of global car sales, a figure predicted to surge to over 10% by 2025. This exponential growth strains the existing battery supply chain, inevitably pushing prices up, especially in the short term.
Moreover, an average EV requires substantially more battery capacity than consumer electronics. A typical EV battery pack, like those in a Tesla Model 3, can be over 50 times larger in capacity than a laptop battery. As automakers ramp up production to meet consumer demand, the strain on battery suppliers becomes even more pronounced.
Energy Storage and Portable Electronics
Beyond vehicles, the rise of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, necessitates effective energy storage solutions. Lithium-ion batteries, known for their efficiency and decreasing price per kWh, are becoming the go-to choice for energy storage systems.
Additionally, the demand from the portable electronics sector, including smartphones, laptops, and wearables, continues to grow. With emerging markets joining the digital revolution and existing markets upgrading devices at a fast pace, this sector alone exerts significant demand pressure on battery supplies.
Limitations in Lithium Supply Chain
While the demand side is surging, the supply side faces challenges. The primary concern is the limited number of lithium and cobalt mines, coupled with geographical concentration of these resources. For instance, the lithium triangle in South America (covering parts of Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia) holds over half the world’s lithium reserves.
Research and Development Costs
The constant evolution and enhancement of lithium-ion battery technology is, in part, due to continuous investments in research and development (R&D). While these investments lead to advancements that improve battery efficiency, lifespan, and safety, they also contribute to the costs associated with battery production.
Investment in New Technologies
In the quest to develop a superior battery, companies are pouring billions into R&D. As of 2020, global R&D spending on battery technologies reached an estimated $6 billion, with a significant chunk directed towards lithium-ion advancements.
This investment isn’t just about enhancing existing technologies but also exploring entirely new chemistries and approaches. For instance, solid-state batteries promise higher energy density and safety levels compared to their liquid-electrolyte counterparts. However, bringing these innovations from the lab to mass production requires immense capital.
Moreover, R&D isn’t just a one-time investment. To remain competitive, companies must continuously innovate, meaning sustained annual investments. While these expenses contribute to the initial high costs of new battery technologies, the eventual benefits, such as greater energy density or faster charging times, provide a competitive edge and long-term cost savings.
Patent Licensing and Royalties
The battery industry is a hotbed for patents. With every technological advancement, companies rush to patent their innovations, aiming to protect and monetize their intellectual property. As a result, manufacturers often find themselves needing to license multiple technologies to produce state-of-the-art batteries.
Environmental and Ethical Concerns
Lithium-ion batteries, often hailed as a solution to reducing carbon emissions, come with their own set of environmental and ethical challenges. Addressing these concerns often adds costs, both direct and indirect, to the production and disposal of these batteries.

Impact on the Environment
The extraction and processing of raw materials for lithium-ion batteries have significant environmental implications. For instance:
- Water Usage: Lithium extraction, especially from brine deposits, is water-intensive. In the Salar de Atacama in Chile, one of the world’s most significant lithium sources, mining consumes around 65% of the region’s water. This has raised concerns over depleting water tables and impacts on local ecosystems.
- Land Degradation: Both lithium and cobalt mining can lead to land degradation. The creation of vast evaporation ponds for lithium extraction in desert regions can alter local landscapes and potentially harm ecosystems.
- Battery Disposal: At the end of their lifecycle, improper disposal of batteries poses environmental hazards. While recycling technologies are improving, as of 2020, less than 5% of lithium-ion batteries are recycled. This is due to the high costs of recycling and technical challenges in extracting valuable materials.
These environmental implications have pushed companies and governments to invest in cleaner extraction technologies and improved recycling methods, all of which add to costs.
Ethical Challenges in Mining Practices
Mining, especially in certain parts of the world, often comes under scrutiny for its ethical implications:
- Child Labor in Cobalt Mining: A significant portion of the world’s cobalt, crucial for many lithium-ion batteries, comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Reports have highlighted the use of child labor in some of these mines. Ethical concerns have led many companies to invest in traceability systems to ensure their supply chains are free from such practices, adding an additional layer of cost.
- Community Rights and Land Acquisition: In several regions, local communities have raised concerns about land rights, where mining activities are undertaken without adequate consultation or compensation. Addressing these concerns often requires negotiations, compensation packages, and sometimes even leads to project delays.
In conclusion, while lithium-ion batteries promise a greener future, producing them comes with its own set of environmental and ethical challenges. Addressing these responsibly often leads to additional costs, reflecting in the final price of the batteries.
Comparative Analysis
A comprehensive understanding of lithium-ion battery costs requires a comparative analysis with other battery technologies. Not only does this give context to the figures but also helps gauge the relative benefits of each battery type.
Lithium Batteries vs. Other Battery Types
Let’s compare some of the core aspects of lithium batteries with other prevalent battery technologies such as Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH).
| Attribute | Lithium-ion | Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) | Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High (150-250 Wh/kg) | Moderate (40-60 Wh/kg) | Moderate (60-120 Wh/kg) |
| Cycle Life | Typically 500-1,000 cycles, newer technologies can reach up to 5,000 cycles | Around 1,500 cycles | 300-1,000 cycles |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Low (~1.5% per month) | High (~20% per month) | Medium (~10% per month) |
| Cost (2020) | Approximately $137/kWh | Lower than Lithium-ion, approx. $50-$70/kWh based on volume and capacity | Slightly cheaper than Lithium-ion, approx. $100-$120/kWh |
While lithium-ion batteries might appear more expensive, their higher energy density and decreasing costs (due to economies of scale and technological advancements) have made them the preferred choice for many applications.
Price Trend Analysis
Historical price trends provide insight into how lithium-ion battery costs have evolved over the years:
| Year | Average Cost per kWh (Lithium-ion) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | $1,160 |
| 2015 | $350 |
| 2020 | $137 |
This sharp decline in prices over the past decade can be attributed to improved manufacturing processes, economies of scale, and significant investments in R&D. However, even with this downward trend, the current costs still reflect the various challenges and complexities discussed in the previous sections.
In conclusion, when analyzed comparatively, lithium-ion batteries offer a compelling mix of performance and decreasing costs. While other battery types might have specific niche applications, the versatility, energy density, and continually declining prices of lithium-ion batteries make them the front runner in many sectors.
