Overview of CNC Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting stands out as a versatile and efficient method for slicing through various materials. It utilizes a plasma torch guided by computer numerical control (CNC) to ensure precise cuts. This advanced technology transforms traditional cutting methods, offering remarkable accuracy and speed.
Principles of Plasma Cutting Technology
Plasma cutting technology harnesses the power of an electrically ionized gas (plasma) to cut through conductive materials. A plasma cutter generates a high-velocity jet of ionized gas heated to an extremely high temperature. This plasma effectively melts the material, while a high-speed gas stream ejects the molten material from the cut. The process is known for its ability to cut through thick and thin metals with a clean and narrow kerf.
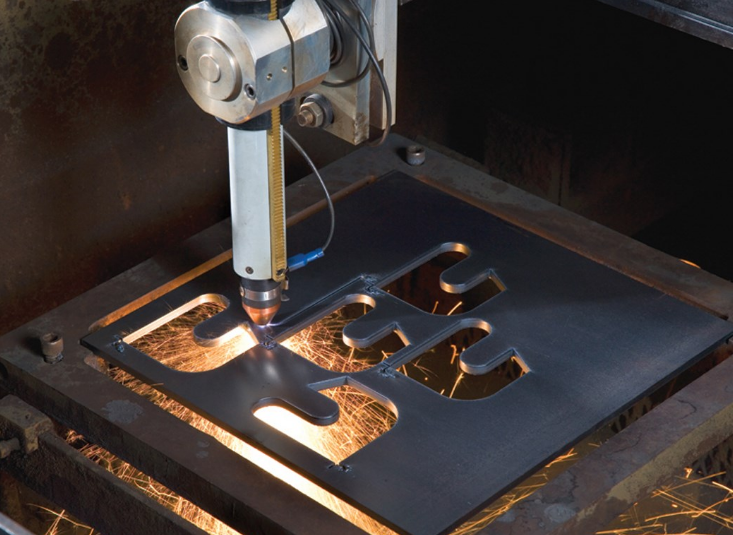

Advantages of CNC in Plasma Cutting
Integrating CNC into plasma cutting amplifies its capabilities. CNC systems bring unparalleled precision, reducing material waste and enhancing cut quality. The automated control allows for intricate patterns and shapes, unachievable by manual methods. CNC plasma cutters often feature a wide range of power options, typically from 20 to 120 amperes, catering to different thicknesses and types of materials. This flexibility is a key advantage, enabling users to handle projects of varying complexity and size.
Moreover, CNC plasma cutting systems are time-efficient. They dramatically speed up the cutting process, sometimes reaching cutting speeds of up to 500 inches per minute, depending on the material and the system’s specifications. This efficiency translates to reduced operational costs and faster project completion times.
Another significant benefit of CNC plasma cutting is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to other cutting methods like laser or waterjet cutting, plasma systems usually have a lower initial investment and operating cost. They are also renowned for their long lifespan, often operating efficiently for many years with proper maintenance, thus offering substantial value over time.
In summary, CNC plasma cutting is a technology that revolutionizes material cutting. It combines speed, precision, and versatility, making it an invaluable tool in various industrial and creative applications. With its ability to handle a wide range of materials and thicknesses, coupled with reduced costs and time efficiency, it stands as a preferred choice for professionals and hobbyists alike.
Metal Cutting Capabilities
CNC plasma cutters excel in cutting a variety of metals, showcasing their adaptability in handling different materials. They cut through metal with precision, maintaining high-quality edges and minimal waste. These machines can handle a wide range of thicknesses, from thin sheets to several inches thick, depending on the cutter’s power and the material’s properties.
Cutting Ferrous Metals (e.g., Steel, Iron)
CNC plasma cutters are particularly effective in slicing through ferrous metals like steel and iron. They can cut steel plates up to 1.5 inches thick with ease, and even thicker plates with more powerful systems. The cutting speed for medium thickness steel, for instance, can reach up to 200 inches per minute, depending on the cutter’s specifications. This capability is crucial in industries like construction and automotive manufacturing, where steel and iron are predominant. The high temperature of the plasma torch ensures a clean cut, minimizing the need for post-cut finishing.
Cutting Non-Ferrous Metals (e.g., Aluminum, Copper)
Non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper also fall within the cutting capabilities of CNC plasma systems. These metals, known for their conductivity and lower melting points, require careful handling. Plasma cutters can efficiently cut aluminum sheets up to 1 inch thick, maintaining precision and speed. For copper, the thickness range is slightly less, but the cut quality remains high. The cutting speed for aluminum and copper is usually faster than for steel, due to their lower melting points. This efficiency is vital in sectors like aerospace and electronics, where these materials are commonly used.
In both ferrous and non-ferrous metal cutting, CNC plasma systems stand out for their cost-effectiveness. They offer a lower cost per cut compared to other methods like laser cutting, especially for thicker materials. The operational costs, including power consumption and consumables like electrodes and nozzles, are relatively low, making them a budget-friendly choice for businesses. Additionally, the longevity of plasma cutters, often lasting several years with proper maintenance, adds to their overall value.
Overall, CNC plasma cutting technology provides a versatile solution for metal cutting needs. It combines speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications in various industries.
Thickness Range and Precision
CNC plasma cutters demonstrate remarkable versatility in handling a wide range of material thicknesses with high precision. They can efficiently cut materials as thin as gauge thickness to several inches thick. This capability allows them to cater to diverse industrial needs, from intricate artistic designs to heavy-duty manufacturing.
Handling Thin Materials: Precision and Limitations
When cutting thin materials, CNC plasma cutters maintain a high level of precision, producing clean and sharp edges. They are ideal for materials like sheet metal, where precision is key, typically cutting up to 0.5 inches thick with excellent accuracy. However, precision can decrease with very thin materials, below 1/20th of an inch, due to the potential for warping and the high intensity of the plasma. In such cases, operators often adjust the power settings to lower amperages, typically around 30 to 50 amperes, to enhance control and minimize heat distortion.
Cutting Thick Materials: Capability and Techniques
For thicker materials, CNC plasma cutters showcase their robust cutting capabilities. They can cut through materials up to 6 inches thick, although the most common range is up to 2 inches for optimal precision and speed. Cutting thicker materials requires higher power settings, often reaching 200 amperes or more. The cutting speed decreases as the material thickness increases, requiring slower rates to ensure thorough cutting and quality edges. Techniques such as multiple-pass cutting and using specific consumables designed for thick materials help achieve the desired results.
In both thin and thick material cutting, the precision of CNC plasma systems is complemented by their cost efficiency. They offer a competitive cost-per-cut ratio, especially for medium to thick materials, compared to alternatives like laser cutting. The operational costs remain manageable due to moderate power consumption and the longevity of consumables. Additionally, the time efficiency of plasma cutting, especially in medium thickness ranges, contributes to overall project cost savings.
Overall, the ability of CNC plasma cutters to handle a wide thickness range with precision makes them invaluable in diverse cutting applications. From intricate designs on thin sheets to robust cuts on thick plates, these systems provide a flexible and cost-effective solution for various industrial needs.
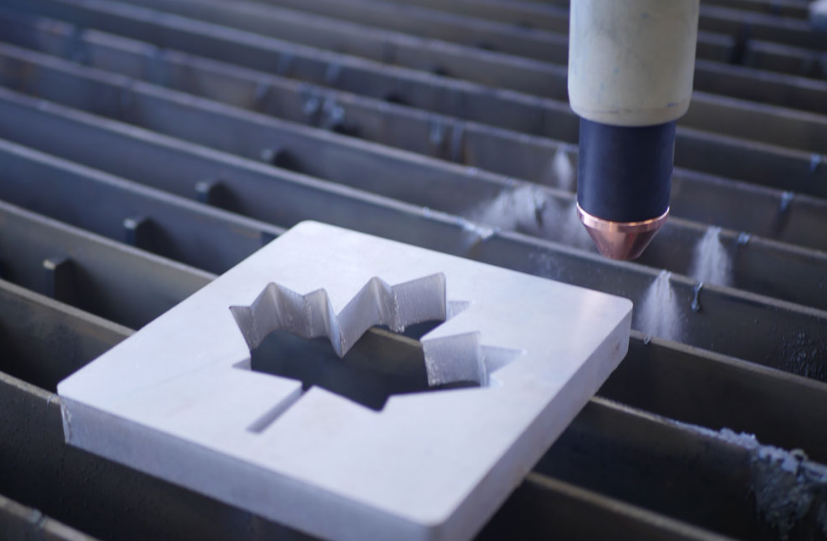
Operational Considerations
In the realm of CNC plasma cutting, operational considerations play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Factors like cutting speed, material preservation, and waste reduction are integral to achieving high-quality results while maximizing cost-effectiveness.
Speed and Efficiency in Different Materials
CNC plasma cutters offer varied cutting speeds depending on the material type and thickness. For instance, cutting thin sheets of steel, about 0.5 inches thick, can reach speeds up to 300 inches per minute. In contrast, thicker materials, like 2-inch steel, require slower speeds, typically around 20 to 30 inches per minute, to ensure a clean cut. The efficiency of CNC plasma cutting also hinges on its power usage, which ranges from 15 kW to 40 kW, depending on the system’s capacity and the material being cut. This efficient power usage contributes to overall cost savings in terms of energy consumption.
Material Preservation and Waste Reduction
Material preservation and waste reduction are crucial aspects of CNC plasma cutting. Advanced CNC technology allows for precise cutting patterns, reducing the amount of scrap and off-cuts. This precision not only conserves material but also lowers the cost of raw materials over time. Additionally, the minimal kerf width in plasma cutting, typically around 1.5 to 2 mm, contributes to less material waste compared to broader cuts from other methods. This aspect is particularly beneficial in industries where material costs are significant, such as in metal fabrication and automotive manufacturing.
These operational considerations highlight the balance CNC plasma cutting systems strike between speed, efficiency, and material utilization. They underscore the technology’s role in promoting sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing processes, making it a valuable asset in various industrial applications.
Safety and Environmental Factors
Safety and environmental considerations are paramount in the operation of CNC plasma cutting systems. These factors dictate the necessary precautions and impact assessments required to ensure a safe and environmentally responsible workspace.
Safety Precautions for Various Materials
When cutting different materials, specific safety precautions are essential. For instance, cutting ferrous metals like steel can produce sparks and slag, necessitating fire-resistant work areas and protective gear. In contrast, cutting non-ferrous metals like aluminum requires ventilation systems to mitigate the risk of inhaling harmful fumes. Operators must always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including eye protection, gloves, and hearing protection. Additionally, maintaining a clean and organized work area reduces the risk of accidents, enhancing overall safety.
Environmental Impact of Cutting Different Materials
The environmental impact of cutting various materials varies. Plasma cutting, especially when cutting metals like steel and aluminum, can emit fumes and gases that may be harmful if not properly ventilated. Implementing effective exhaust systems is crucial to minimize air pollution. The use of electricity in plasma cutting, typically ranging from 15 to 40 kW, also factors into its environmental footprint. However, compared to other cutting methods like oxy-fuel cutting, plasma systems often have a lower environmental impact due to their higher energy efficiency and reduced gas emissions.
These safety and environmental factors emphasize the importance of responsible operation and maintenance of CNC plasma cutting systems. They ensure not only the safety of the operators but also contribute to minimizing the ecological impact of industrial processes.
