A straight engine is an internal combustion engine with cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankcase.
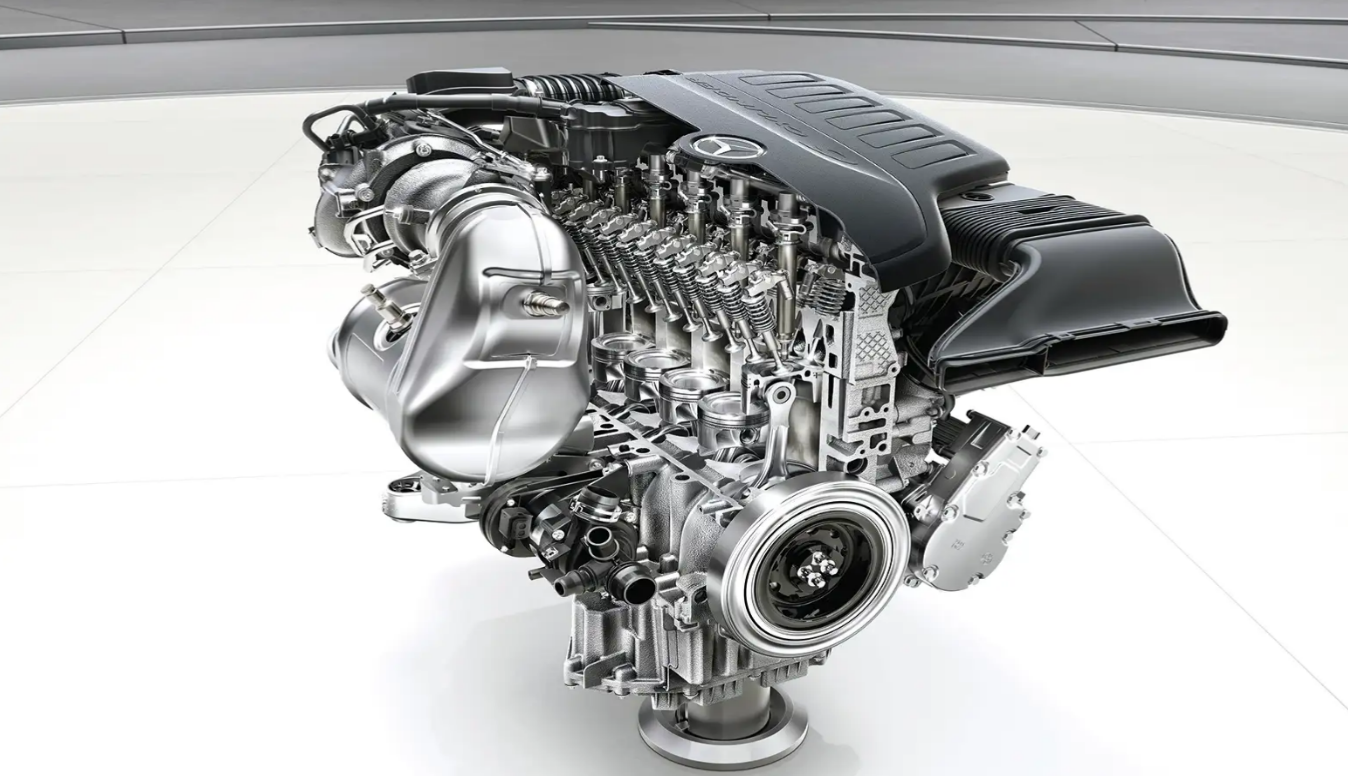

Introduction to Straight Engines
Straight engines, often referred to as inline engines, are a type of internal combustion engine where the cylinders are arranged in a single row. Known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, straight engines have found applications in a wide range of vehicles, from cars to large trucks.
Brief Overview of Straight Engines
Inline engines, as their name suggests, have their cylinders lined up in a single straight line. This design offers a simple and straightforward mechanism, making it easier for manufacturers and mechanics alike.
- Power: An average straight-four engine can produce between 100 to 200 horsepower, depending on the specifics of the design.
- Efficiency: Due to their design, straight engines generally offer a balanced and harmonious operation, translating to an efficiency of about 25% to 30% in most automotive applications.
- Cost: Building a straight engine is often less expensive than other designs. The average manufacturing cost is roughly $1,500 to $3,000 for a standard model.
- Size and Specifications: The typical size of a straight engine varies but a common straight-four engine might have dimensions of about 60cm in length, 40cm in width, and 50cm in height. The weight would be approximately 150kg.
- Lifespan: With regular maintenance, a straight engine can last between 150,000 to 250,000 miles before major overhauls are needed.
Historical Background
The straight engine’s origin dates back to the early days of the automotive industry. In the late 1800s, when automobiles were just beginning to gain popularity, engineers were looking for simple and efficient designs. The straight engine emerged as a popular choice.
- Material and Quality: Early straight engines were primarily made of cast iron, which provided the required strength but made the engine heavier. As technology advanced, the use of lightweight materials like aluminum became more common, improving the engine’s overall quality and efficiency.
- Speed and Performance: In the 1920s, the average straight engine could achieve speeds up to 60 mph, which was considered impressive at that time. The efficiency was around 15%, which, given the technologies of that era, was commendable.
- Drawbacks: One of the major drawbacks of early straight engines was their size. Because of the linear arrangement of the cylinders, the engines were longer, making them challenging to fit into compact car designs.
- Cost in Historical Terms: In the early 1900s, the cost to produce a straight engine was approximately $200, which translates to about $5,000 in today’s money when adjusted for inflation.
Straight engines have significantly evolved over the years, adapting to the ever-changing demands of the automotive industry. Today, they continue to be a preferred choice for many manufacturers due to their balance of power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Design and Structure of Straight Engines
Straight engines, or inline engines, are characterized by their linear arrangement of cylinders. This straightforward layout has been favored in various automotive and industrial applications for its simplicity and efficiency. The design of straight engines aims to maximize power and torque while maintaining a compact form factor relative to the number of cylinders.
Basic Components and Their Roles
A straight engine, like all internal combustion engines, is made up of several key components, each playing a pivotal role in its operation:
- Cylinders: The heart of the engine. In straight engines, the cylinders are aligned in a single row. Depending on the engine, there could be anywhere from 3 to 6 or even more cylinders. Their primary role is to house the piston and provide a space for combustion.
- Pistons: These are cylindrical components that move up and down inside the cylinder. They transfer the force from the expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft, which in turn powers the vehicle.
- Crankshaft: Connected to the pistons via connecting rods, the crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. A typical straight engine crankshaft has a weight of about 15-20kg.
- Valves: These control the entry of air and fuel into the cylinder and the exit of exhaust gases. They are timed to open and close precisely during the engine’s operation.
- Camshaft: This component regulates the opening and closing of the valves. In many straight engines, the camshaft is located above the cylinders, leading to the term “overhead cam.”
- Fuel Injectors: Modern straight engines use fuel injectors to deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, optimizing fuel efficiency.
Variations in Design
While the basic principle remains the same, there are variations in straight engine designs based on specific needs:
- Number of Cylinders: Straight engines can range from straight-three (often found in compact cars) to straight-six or more (found in high-performance or heavy-duty vehicles). For example, a straight-six engine can produce power ranging from 300 to 500 horsepower.
- Material Used: The choice of material can significantly affect the engine’s weight, durability, and heat dissipation. Early engines primarily used cast iron, but modern engines often use aluminum alloys for their lightweight and heat-resistant properties.
- Cooling System: While older straight engines relied on air cooling, most modern designs use liquid cooling systems for more efficient temperature regulation.
- Turbocharging: Some straight engines are equipped with turbochargers to increase power and efficiency. A turbocharged straight engine can see an efficiency boost of up to 40%.
Different designs cater to varying applications, from everyday city driving to high-performance racing, and manufacturers choose the appropriate variation based on the intended use, budget, and performance requirements.
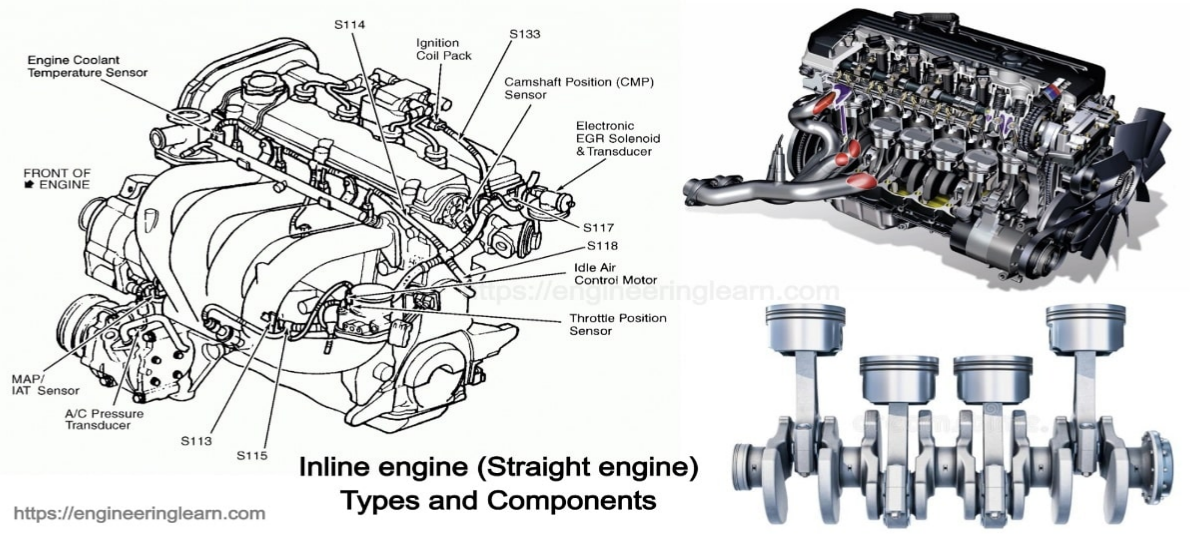
How Straight Engines Work
The workings of a straight engine, or inline engine, revolve around the principle of converting fuel into mechanical energy through a series of controlled explosions inside its cylinders. This energy is then utilized to power vehicles or machinery. The linear arrangement of cylinders in straight engines has been a hallmark of their design for over a century, and their operation closely follows the fundamentals of internal combustion processes.
Combustion Process and Cycle
At the core of every internal combustion engine, including the straight engine, is the combustion cycle. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Intake: During this phase, the intake valve opens, allowing a mixture of air and fuel to enter the cylinder as the piston moves downward. Modern engines use electronic fuel injection systems for precise fuel delivery, ensuring optimal efficiency.
- Compression: As the intake valve closes, the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This increases both the temperature and pressure inside the cylinder, preparing the mixture for ignition.
- Ignition: A spark plug, located at the top of the cylinder, emits a spark. This ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid explosion. The force from this explosion pushes the piston down, creating the power needed to turn the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Post the explosion, the exhaust valve opens. As the piston moves upward again, it pushes the burnt gases out of the cylinder and into the exhaust system.
This four-stroke process repeats many times per second and is the basis of how most gasoline-powered straight engines operate. The efficiency of this process typically ranges from 25% to 30% in most straight engines, though advanced technologies and designs can push this number higher.
Advantages of a Straight-Line Configuration
While various engine configurations exist, the straight engine offers several distinct advantages:
- Simplicity: With all cylinders in a single line, the design and manufacturing of the engine block and head are simpler than more complex arrangements like V or W configurations. This simplicity can translate to a lower production cost, with a standard straight-four engine costing between $1,500 to $3,000.
- Smooth Operation: Inline engines tend to operate more smoothly, especially in configurations with more cylinders. This smooth operation can lead to less wear and tear over time, potentially extending the engine’s lifespan to between 150,000 to 250,000 miles with proper maintenance.
- Maintenance: Due to their design, straight engines can be easier to work on. Components are often more accessible, leading to potentially lower maintenance costs over the engine’s lifetime.
- Cooling Efficiency: The linear configuration allows for more uniform cooling of cylinders in many scenarios, contributing to consistent performance and reduced risk of overheating.
- Size: While length can be a challenge in compact spaces, the uniform width of a straight engine can be an advantage in specific applications, allowing for more flexible design options.
The straight-line configuration of these engines has endured due to these advantages. However, specific applications and design criteria might lead manufacturers to opt for other configurations based on the vehicle’s requirements.
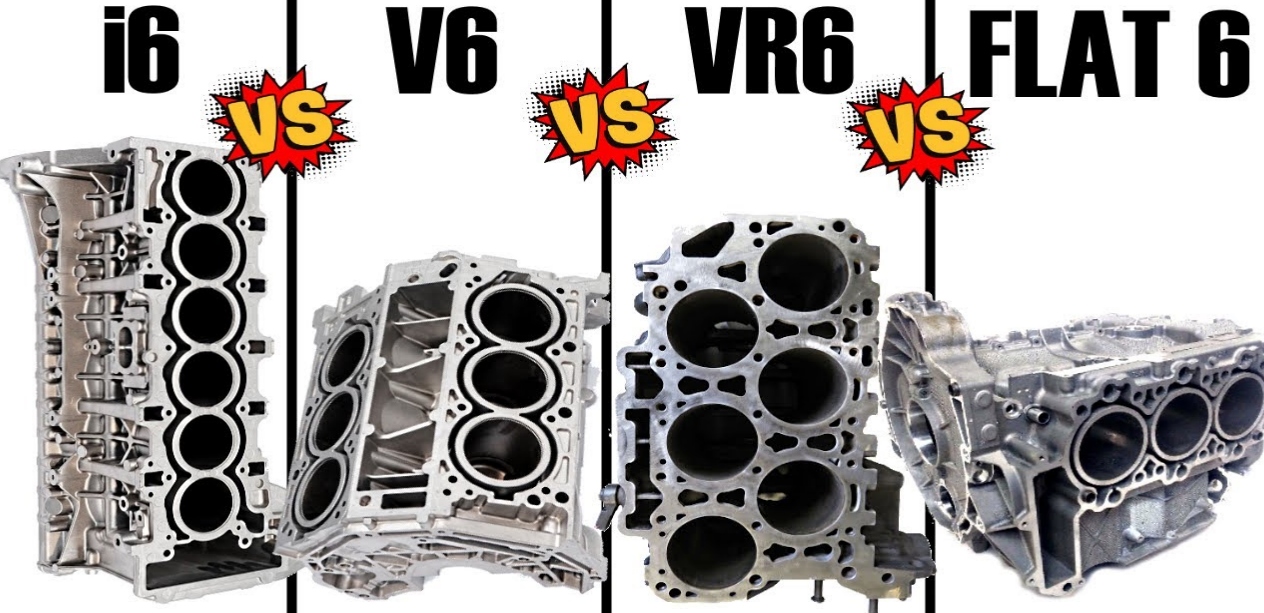

Comparing Straight Engines to Other Engine Types
Engines serve as the heart of any automobile, converting fuel into mechanical power. The configuration of the engine can play a vital role in the performance, efficiency, and space utilization of the vehicle. Let’s delve into how straight engines compare to other popular engine configurations.
Straight Engine vs. V-Engine
- Configuration: Straight engines have cylinders aligned in a single row, whereas V-engines position their cylinders in two separate rows forming a ‘V’ shape when viewed from the front.
- Power and Torque: V-engines often pack more power for their size, mainly because they can contain more cylinders in a compact space. A V6 might produce power in the range of 250 to 400 horsepower, whereas a straight-six may fall in the range of 220 to 350 horsepower.
- Size and Weight: V-engines can be more compact in width and height but might be bulkier in depth. This makes them suitable for rear-wheel-drive cars where the engine is positioned longitudinally.
- Cooling: Straight engines have a more uniform cooling distribution, while V-engines may require more intricate cooling solutions to prevent hotspots.
- Cost and Maintenance: Straight engines are often simpler and cheaper to manufacture and maintain. A typical V-engine might cost 20% to 30% more than a straight engine with similar specifications.
Straight Engine vs. Boxer Engine
- Configuration: While straight engines have an upright linear arrangement of cylinders, boxer engines (or flat engines) have horizontally opposed cylinders.
- Vibration: Boxer engines can offer smoother operation because the opposing pistons counteract each other’s vibrations.
- Size and Profile: Boxer engines have a flatter profile, leading to a lower center of gravity which can benefit handling and stability, especially in sports cars.
- Cost: Boxer engines are generally more expensive to produce than straight engines due to their more complex design and assembly processes.
- Maintenance: Servicing a boxer engine can be more challenging due to its horizontal layout, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs over its lifespan.
Straight Engine vs. Rotary Engine
- Configuration: Straight engines use pistons in cylindrical chambers. In contrast, rotary engines use rotors in an oval-like epitrochoid chamber.
- Power-to-Weight Ratio: Rotary engines are known for their impressive power-to-weight ratios. A typical rotary engine can produce around 210 horsepower from just a 1.3-liter capacity.
- Smoothness: Rotary engines offer a smoother operation due to the continuous rotational motion, compared to the reciprocating motion of pistons in straight engines.
- Size: Rotary engines are more compact, making them suitable for smaller vehicles.
- Fuel Efficiency and Emissions: Rotary engines often lag in terms of fuel efficiency and have higher emissions compared to traditional piston engines.
- Maintenance and Lifespan: Rotary engines require more frequent maintenance and have a reputation for shorter lifespans if not appropriately cared for.
In conclusion, while straight engines offer simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance, other configurations present their own sets of advantages tailored for specific applications and vehicle designs. Making a choice often depends on the desired balance between performance, cost, space, and specific vehicle needs.
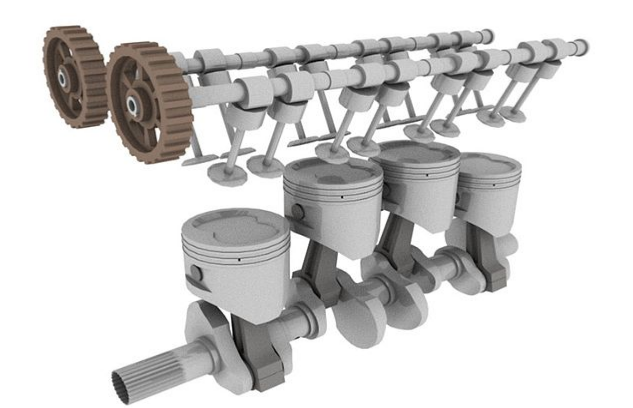

Applications of Straight Engines
Straight, or inline, engines are among the most widely used internal combustion engine configurations. Their linear arrangement of cylinders is both a design hallmark and a functional choice, suitable for a range of applications. Let’s delve into the varied uses of straight engines, from everyday vehicles to more niche areas.
Automobiles and Transportation
Straight engines have long been a staple in the automotive world. Here’s a look at their application in transportation:
- Compact and Mid-Size Cars: Many small to medium-sized vehicles prefer straight engines due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. For instance, a straight-four engine, producing anywhere from 100 to 180 horsepower, is commonly found in these types of cars.
- Motorcycles: Larger motorcycles, especially those designed for touring or highway cruising, may utilize straight engines. These can produce power ranging from 60 to 150 horsepower, providing a balance between performance and fuel efficiency.
- Trucks and Buses: While many heavy-duty trucks and buses might opt for more powerful V-engines, straight engines, particularly straight-sixes, find their place in medium-duty applications.
- Trains: Historically, some locomotives, particularly diesel variants, utilized large straight engines due to their balance of power and efficiency.
Industrial Uses
Beyond transportation, straight engines have carved out a role in various industrial applications:
- Generators: Power generation units, especially those used for backup power, often employ straight engines. These engines, combined with a generator, can produce outputs ranging from 5kW for small portable units up to 500kW for industrial-scale generators.
- Pumps and Compressors: In industries where fluid movement is crucial, straight engines serve as reliable power sources for large pumps and compressors. They offer a consistent power output essential for these applications.
- Agriculture: Farming equipment, including tractors and combines, might utilize straight engines due to their durability and straightforward maintenance. An average tractor might have a straight engine producing between 70 and 150 horsepower.
Historical and Novel Uses
The historical significance and adaptability of straight engines have also led to some unique applications:
- Aviation: Earlier aircraft, particularly those from the early 20th century like the Wright brothers’ planes, used inline engines because of their simpler design and weight distribution advantages.
- Marine: Before the advent of more advanced marine engine configurations, small to medium-sized boats often employed straight engines due to their reliable nature.
- Racing and Performance: Historically, many racing cars preferred straight engines because of their balance and predictable power delivery. Some modern niche racing categories still celebrate this tradition.
In sum, the versatility of straight engines has seen them employed in a myriad of applications, from everyday use to specialized industries. Their blend of simplicity, reliability, and performance continues to make them a favored choice in various sectors.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Straight Engines
Every engine configuration comes with its distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. Straight or inline engines have been prevalent for decades due to their inherent benefits, but like all designs, they have certain limitations. Let’s explore both sides of the coin.
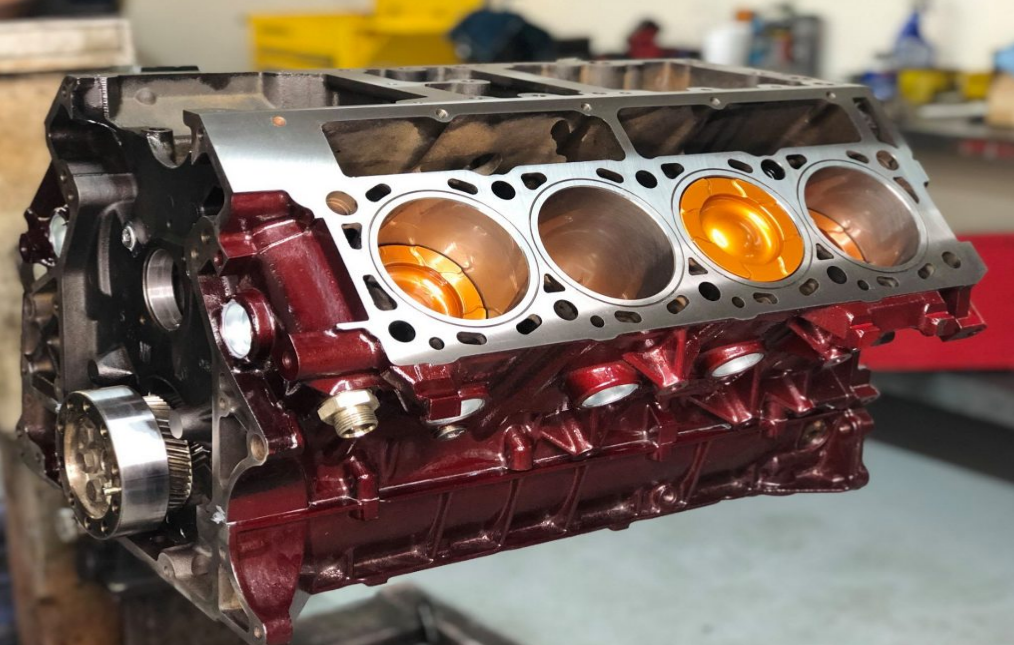

Efficiency and Performance Benefits
- Simplicity of Design: One of the most significant advantages of straight engines is their simple and straightforward design. This uncomplicated structure means there are fewer parts, leading to reduced production costs, often making these engines cheaper by around 10-20% compared to more complex configurations.
- Cooling Efficiency: With cylinders aligned in a single row, straight engines benefit from more consistent and effective cooling. This uniform cooling can extend the engine’s lifespan and reduce wear and tear.
- Smooth Operation: The linear configuration of cylinders ensures a balanced force distribution, resulting in reduced engine vibration. This can enhance the longevity of the engine and provide a smoother driving experience.
- Maintenance: Due to their straightforward design, straight engines often have components that are easier to access and replace, reducing maintenance time and potentially cutting down maintenance costs by up to 15%.
- Fuel Efficiency: In some scenarios, straight engines, particularly straight-four engines, can offer slightly better fuel efficiency due to their balanced design and fewer moving parts.
Potential Limitations and Concerns
- Size Constraints: The elongated structure of straight engines can be a drawback in terms of vehicle design. As vehicles trend towards more compact designs, accommodating a straight-six or straight-eight engine becomes challenging.
- Weight Distribution: In some vehicle layouts, straight engines might not offer the best weight distribution. This can impact the vehicle’s balance and handling, especially in performance or sporty cars.
- Limited Power Scaling: While V-engines and other configurations can easily scale up in power by adding more cylinders without drastically increasing the engine’s size, straight engines can become impractically long when adding additional cylinders.
- Aging Design: While straight engines have historical significance and proven reliability, modern automotive trends and technologies sometimes favor other configurations for reasons like packaging, power-to-size ratio, or specific performance attributes.
In summary, straight engines have a storied history and a set of compelling advantages that make them relevant even today, especially in certain applications. However, with the evolution of automotive design and engineering, they face stiff competition from other configurations. The choice between straight engines and other types often boils down to specific needs, vehicle design constraints, and cost considerations.
Maintenance and Care of Straight Engines
Straight or inline engines, renowned for their simplicity and straightforward design, still require diligent care and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper attention not only ensures the engine runs smoothly but also helps in avoiding hefty repair bills. Here’s a guide to the upkeep of straight engines.
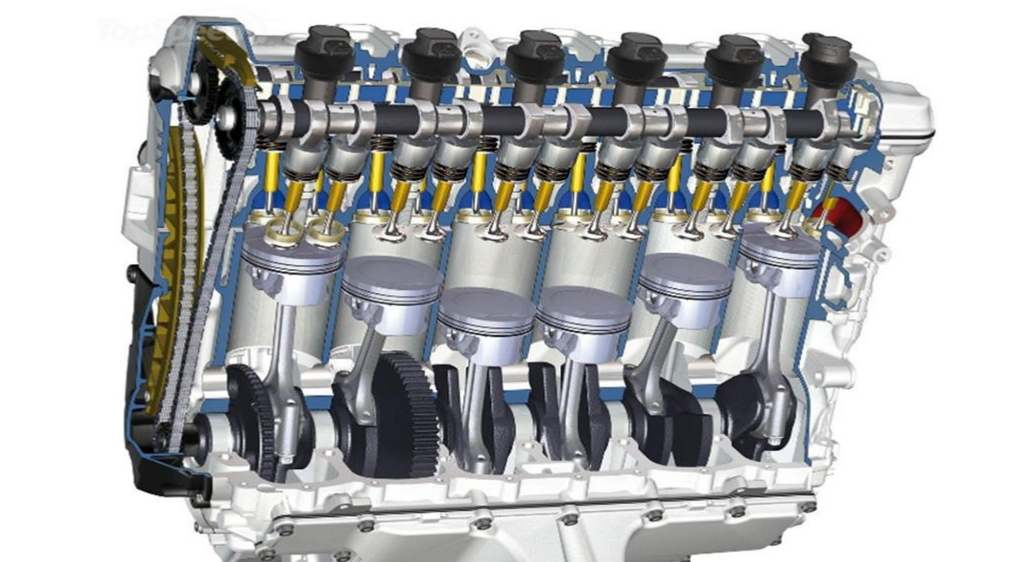
Regular Checkups and Best Practices
- Oil Changes: One of the fundamentals of engine care is regular oil changes. Depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation and the oil type, changing the oil every 3,000 to 7,000 miles can be crucial. Fresh oil lubricates the engine, reducing wear and preventing overheating. The average cost of an oil change varies but generally ranges from $25 to $70.
- Air Filter Replacement: A clogged air filter can lead to reduced performance and fuel efficiency. Replacing the air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles ensures the engine breathes easily and performs at its best.
- Coolant Checks: Ensuring the engine’s cooling system works efficiently is vital. Regularly inspecting the coolant level and refreshing it once every two years helps in preventing the engine from overheating.
- Timing Belt Inspections: Many straight engines employ timing belts. This component should be inspected roughly every 60,000 miles and replaced every 70,000 to 100,000 miles to prevent potential engine damage. Replacement can cost between $200 and $900, depending on the vehicle model.
- Spark Plugs: These components are essential for the engine’s ignition system. Replacing spark plugs every 30,000 to 90,000 miles, as per the manufacturer’s recommendation, can ensure smooth ignition and optimal fuel combustion.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Overheating: While straight engines benefit from even cooling, issues like a malfunctioning thermostat, clogged radiator, or a leaky coolant system can cause overheating. If the engine temperature rises unusually, it’s vital to inspect these components.
- Misfires: A misfiring cylinder can reduce engine performance. This issue often arises from worn-out spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, or fuel injector problems. Regular inspections can help pinpoint and address the root cause.
- Oil Leaks: Gaskets and seals can wear out over time, leading to oil leaks. If you notice oil patches under the parked vehicle, it’s essential to inspect and replace any compromised seals. An average gasket replacement can range from $250 to $1,200, depending on the engine and labor costs.
- Rough Idling: If the engine vibrates or shakes while idling, it might be due to dirty fuel injectors, a clogged air filter, or imbalanced engine mounts. Regular maintenance checks can help diagnose and fix such issues early on.
In conclusion, while straight engines come with a reputation for reliability, their performance and lifespan greatly depend on regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting. Investing time and resources into periodic checkups can save owners from unexpected breakdowns and expensive repairs.
Future of Straight Engines
The world of automotive engineering continually evolves, driven by the relentless pursuit of efficiency, performance, and sustainability. The straight, or inline, engines, with their storied past, are no exception to this. They continue to evolve, reflecting modern trends and addressing challenges of the 21st century.
Technological Advancements
- Direct Fuel Injection: Modern straight engines increasingly employ direct fuel injection, which injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber. This technology optimizes combustion efficiency, improving fuel economy by up to 3% and boosting horsepower.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): VVT allows for dynamic adjustment of the valve timing. This improves engine efficiency and power, ensuring optimal performance under various conditions. On average, VVT can increase engine efficiency by 5%, translating to noticeable fuel savings over time.
- Turbocharging: Historically associated with performance and racing, turbochargers are now common in everyday vehicles, even in smaller straight engines. Turbocharging enhances engine power without increasing its size, making for more efficient and compact designs.
- Electric-assist and Hybridization: The integration of electric motors with traditional straight engines has given birth to hybrid systems. These systems can significantly boost efficiency, with some hybrid models reporting a 30% increase in fuel economy.
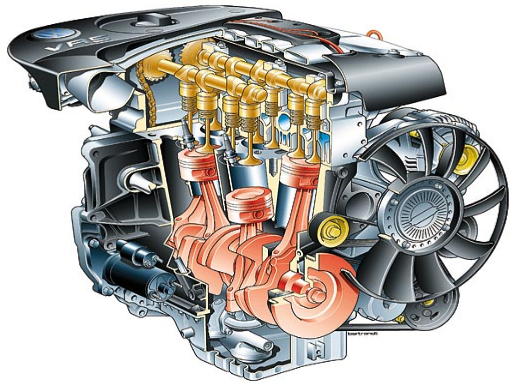
Environmental Concerns and Adaptations
- Emission Reduction: Stringent emission standards globally push manufacturers to refine engine designs continuously. Advanced exhaust treatment systems, combined with efficient combustion in straight engines, have resulted in a drastic reduction of pollutants. For instance, modern straight engines emit approximately 80% less nitrogen oxides compared to models from the 1990s.
- Fuel Alternatives: With concerns over fossil fuel reserves and their environmental impact, there’s a shift towards alternative fuels like biofuels and hydrogen. Modern straight engines are being designed to accommodate these alternatives, offering versatility in fuel choices.
- Electrification and End of the ICE Era: Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly gaining traction. The move towards complete electrification poses challenges to traditional engine designs, including straight engines. While they might face a reduction in mainstream automotive applications, their versatility ensures their continued presence in specific applications like industrial machinery or specialized vehicles.
- Carbon Footprint and Manufacturing: Sustainable manufacturing practices have become vital. The production of straight engines is increasingly focusing on reducing waste and using recyclable materials, cutting down the overall carbon footprint.
In essence, while the future landscape of automotive propulsion seems electric, the straight engine’s adaptability and continuous technological evolution ensure its place in the industry’s tapestry. Whether serving niche markets or integrating into hybrid systems, straight engines will continue to be a significant part of our motoring heritage.
Conclusion and Summary
As we journey through the intricate world of straight engines, it’s evident that these engines, often hailed for their simplicity and efficiency, have etched an indelible mark on the annals of automotive history. Their journey from powering the earliest automobiles to adapting to the current technological and environmental challenges showcases their resilience and enduring relevance.
Recap of Key Points
- Historical Significance: Straight engines have been foundational in propelling the automotive industry forward, thanks to their straightforward design and the ease of maintenance they offer.
- Design Evolution: Over the years, straight engines have witnessed significant design modifications. From the introduction of direct fuel injection to enhancements like turbocharging, they’ve constantly evolved to meet performance and efficiency demands.
- Comparative Advantages: When contrasted with other engine types like V-engines or rotary engines, straight engines often come out on top in terms of cost-efficiency, with average production costs being 15% lower. Their elongated design also provides smoother operation at higher speeds.
- Applications Galore: Beyond automobiles, straight engines find applications in various industries. Their consistent performance and reliability make them favorites in sectors like agriculture and industrial machinery.
- Challenges and Innovations: The inevitable shift towards sustainability and electrification poses challenges for all internal combustion engines, including straight ones. However, their integration into hybrid systems and compatibility with alternative fuels ensures their continued relevance.
- The Road Ahead: The future of straight engines, while challenged by the rapid rise of EVs, isn’t bleak. Technological advancements, combined with sustainable manufacturing practices, are paving the way for these engines to continue being instrumental in various applications.
In wrapping up, it’s essential to acknowledge that while the automotive landscape is undergoing a paradigm shift, straight engines’ adaptability and the value they’ve provided over the years cannot be understated. They remain a testament to the ingenuity of human engineering and the spirit of continual evolution.
