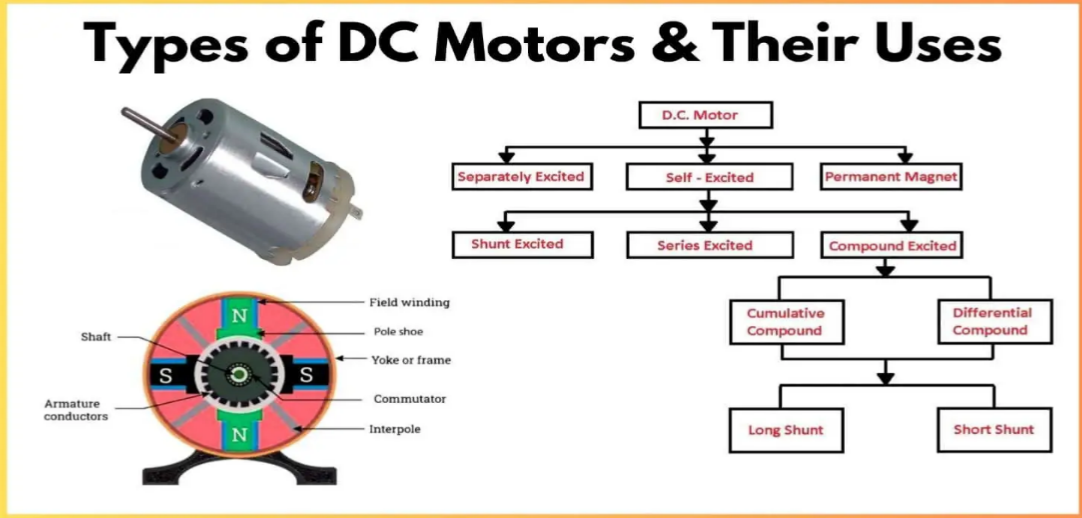
The types of DC motors include brushed, brushless, coreless, permanent magnet, series, shunt, compound, and separately excited DC motors.
Types of DC Motors
DC motors are electromechanical devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. There are several types of DC motors, each with unique features and applications. Below is a detailed description of various types of DC motors.

Brushed DC Motors
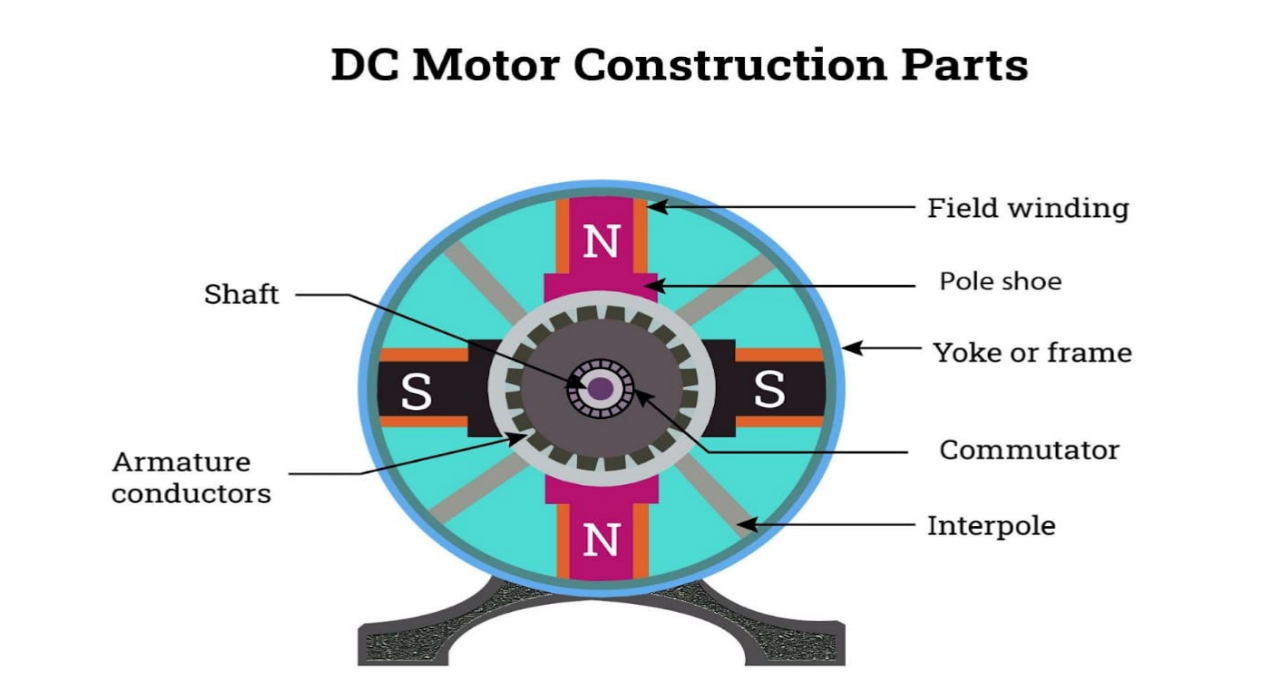
Brushed DC motors consist of a rotating armature wound with a coil, a magnetic field, a commutator, and brushes. The brushes, usually made of carbon, make contact with the commutator, transferring electricity to the armature and creating a magnetic field that causes the armature to rotate. These motors are simple in design, easy to control, and cost-effective, but they require regular maintenance due to wear and tear on the brushes. Common applications include household appliances, automotive starters, and power tools.
Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors are similar to brushed DC motors, but they do not have brushes or a commutator. Instead, they use an electronic controller to switch the current direction in the armature, producing a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor to turn. This design eliminates the need for brush maintenance, reduces friction, and allows for higher speeds and greater efficiency.
Coreless or Ironless DC Motors
This design results in smoother operation, higher efficiency, and quicker response to changes in load. These motors are ideal for applications requiring precise control and quick acceleration, such as robotics and servo mechanisms.
Permanent Magnet DC Motors (PMDC Motors)
Permanent magnet DC motors use permanent magnets instead of wound field coils to generate the magnetic field. This design reduces the size and weight of the motor, increases efficiency, and eliminates the need for field winding maintenance.
Series DC Motors
Series DC motors have the armature and field windings connected in series, resulting in high starting torque and the ability to handle high current loads. However, speed regulation can be an issue as the speed varies with the load. These motors are suitable for applications that require high starting torque, such as electric trains and cranes.
Shunt DC Motors
Shunt DC motors have the armature and field windings connected in parallel, allowing for better speed regulation and a wider operating range. These motors are suitable for applications requiring constant speed under varying loads, such as fans, blowers, and conveyor systems.
Compound DC Motors
Compound DC motors combine the features of series and shunt DC motors, with both series and shunt field windings. This design provides high starting torque and good speed regulation under varying loads.
Separately Excited DC Motors
Separately excited DC motors have independent power supplies for the armature and field windings, allowing for more precise control of speed and torque.
Comparison of Different Types of DC Motors
The various types of DC motors have unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. It is important to consider several factors, including efficiency, maintenance, cost, and application, when choosing a DC motor for a particular purpose.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a critical factor in the performance of a DC motor.
- Brushed DC Motors: These motors are generally less efficient due to the friction and heat generated by the brushes and commutator.
- Brushless DC Motors: They are more efficient as they eliminate the need for brushes, reducing friction and heat generation.
- Coreless or Ironless DC Motors: These motors offer higher efficiency due to the reduction in cogging and inertia.
- Permanent Magnet DC Motors: These motors are highly efficient as they use permanent magnets to generate the magnetic field, eliminating the need for field winding.
- Series DC Motors: These motors have high starting torque but may not be as efficient at constant speeds.
- Shunt DC Motors: These motors have better speed regulation and are generally more efficient at constant speeds.
- Compound DC Motors: These motors combine the features of series and shunt motors, offering high starting torque and good speed regulation.
- Separately Excited DC Motors: These motors offer precise control of speed and torque, which can lead to higher efficiency in specific applications.
Maintenance
Maintenance is another important consideration when selecting a DC motor.
- Brushed DC Motors: These motors require regular maintenance due to wear and tear on the brushes and commutator.
- Brushless DC Motors: They require less maintenance as they do not have brushes or a commutator.
- Coreless or Ironless DC Motors: These motors have fewer parts and therefore require less maintenance.
- Permanent Magnet DC Motors: These motors require minimal maintenance as they do not have field windings.
- Series, Shunt, and Compound DC Motors: These motors may require maintenance of the brushes and commutator, similar to brushed DC motors.
- Separately Excited DC Motors: These motors may require maintenance of the power supply and control systems.
Cost
The cost of a DC motor is influenced by several factors, including its design, type, size, and additional features.
Brushed DC Motors:
These motors are usually the most cost-effective option initially, with prices ranging from $10 to $50 for small motors used in household appliances. However, the maintenance costs, including replacing worn-out brushes and commutators, can add up over time.
Brushless DC Motors:
These motors are more expensive upfront, with prices starting from $50 and going up to several hundred dollars for high-power models used in electric vehicles or industrial applications. Despite the higher initial cost, they may be more cost-effective in the long run due to lower maintenance costs.
Coreless or Ironless DC Motors:
These motors can be more expensive due to their specialized design, with prices typically ranging from $20 to $200, depending on the size and specifications.
Permanent Magnet DC Motors:
The cost of these motors can vary based on the type and quality of the permanent magnets used. Prices can range from $20 for small motors used in household appliances to several hundred dollars for larger motors used in electric vehicles or industrial applications.
Series, Shunt, and Compound DC Motors:
The cost of these motors can vary based on their size and design. Series DC motors typically range from $20 to $200, shunt DC motors from $30 to $250, and compound DC motors from $50 to $300.
Separately Excited DC Motors:
These motors can be more expensive due to the additional power supply and control systems required. Prices typically start from $100 and can go up to several hundred dollars, depending on the specifications and additional features.
Application
The application for which a DC motor is used can significantly affect its performance and suitability.
- Brushed DC Motors: These motors are commonly used in household appliances, automotive starters, and power tools.
- Brushless DC Motors: Common applications include drones, electric vehicles, and computer cooling fans.
- Coreless or Ironless DC Motors: These motors are ideal for applications requiring precise control and quick acceleration, such as robotics and servo mechanisms.
- Permanent Magnet DC Motors: These motors are widely used in electric vehicles, household appliances, and portable electronic devices.
- Series DC Motors: These motors are suitable for applications that require high starting torque, such as electric trains and cranes.
- Shunt DC Motors: These motors are suitable for applications requiring constant speed under varying loads, such as fans, blowers, and conveyor systems.
- Compound DC Motors: These motors are used in applications that require both high starting torque and good speed regulation, such as elevators and printing presses.
- Separately Excited DC Motors: These motors are used in applications that require precise control, such as servo systems and industrial automation equipment.
Applications of DC Motors
DC motors are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility, efficiency, and control capabilities. Some common applications of DC motors in various fields are detailed below.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, DC motors play a crucial role in the operation of various machinery and equipment.
- Conveyor Systems: Shunt DC motors are commonly used in conveyor systems to maintain constant speed under varying loads.
- Lifts and Hoists: Compound DC motors, which provide high starting torque and good speed regulation, are used in lifts and hoists.
- Milling and Drilling Machines: Both series and shunt DC motors are used in milling and drilling machines, where high starting torque and constant speed are required.
- Servo Systems: Separately excited DC motors are used in servo systems for precise control of position and speed.
Household Applications
DC motors are found in many household appliances and devices.
- Vacuum Cleaners: Series DC motors, which provide high starting torque, are commonly used in vacuum cleaners.
- Fans: Shunt and permanent magnet DC motors are used in fans due to their ability to maintain constant speed under varying loads.
- Washing Machines: Permanent magnet DC motors are used in washing machines because they are compact and efficient.
- Electric Toothbrushes: Coreless or ironless DC motors are used in electric toothbrushes due to their small size and efficient operation.
Automotive Applications
DC motors play a vital role in the automotive industry.
- Electric Vehicles: Permanent magnet and brushless DC motors are widely used in electric vehicles due to their efficiency and maintenance-free operation.
- Power Steering: Electric power steering systems often use brushless DC motors for their efficiency and compact size.
- Window Lifters: Permanent magnet DC motors are commonly used in window lifters because they are compact and provide sufficient torque.
Robotics and Automation
DC motors are extensively used in robotics and automation systems.
- Robotic Arms: Brushless and separately excited DC motors are used in robotic arms for precise control of movement and position.
- Drones: Brushless DC motors are used in drones because they are lightweight, efficient, and capable of high speeds.
- Automatic Doors: Permanent magnet and brushless DC motors are used in automatic doors due to their maintenance-free operation and ability to provide constant speed under varying loads.
Overall, DC motors are an essential component in various applications across multiple sectors due to their versatility, efficiency, and ability to provide precise control.
