No, extrusion and molding are different processes; extrusion pushes material through a die, while molding uses a mold to shape material.
Understanding Extrusion and Molding Processes
Definition and Basics of Extrusion
Extrusion is a manufacturing process where material is pushed through a die to create objects with a fixed, continuous cross-sectional profile. This process is widely used for both metals and plastics.
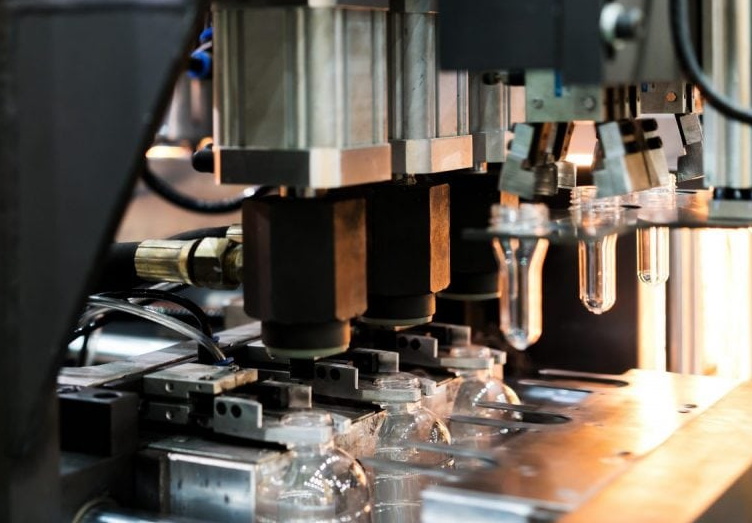

Process Mechanics: Involves feeding material into a machine where it’s heated and then forced through a die, shaping it into a continuous profile.
Temperature Range: Varies significantly based on the material. For instance, aluminum extrusion can occur at temperatures around 350°C to 500°C.
Production Speed: Can range from 0.5 to 100 meters per minute, depending on the material’s characteristics and the complexity of the cross-section.
Energy Consumption: Typically requires 20 to 200 kW.
Cost Factors: High initial setup costs for dies and machinery, but effective for high-volume production with low per-unit costs.
Definition and Basics of Molding
Molding is a diverse manufacturing process that involves shaping material in a mold. It includes several methods, such as injection molding, blow molding, and compression molding.
Process Variations:
Injection Molding: Melting plastic and injecting it into a mold cavity.
Blow Molding: Used for hollow objects, where air blows the plastic into the mold’s shape.
Compression Molding: Placing material into a heated mold, then applying pressure.
Temperature Requirements: For plastics, injection molding temperatures can range from 180°C to 280°C.
Cycle Time: Depending on the product’s size and complexity, cycle times can vary from a few seconds to several minutes.
Energy Consumption: Generally lower than extrusion, with injection molding machines consuming between 4 kW and 20 kW.
Cost Factors: Molds can be expensive to fabricate, but are cost-effective for mass production due to low per-unit costs and minimal waste.
For more detailed insights, the Wikipedia page on Extrusion and Injection Molding are excellent resources.
Comparative Analysis of Extrusion and Molding
Process Methodologies: Differences and Similarities
| Aspect | Extrusion | Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process Mechanics | Material pushed through a die | Material shaped in a mold |
| Production Speed | Ranges from 0.5 to 100 m/min | Cycle times from a few seconds to minutes |
| Energy Consumption | 20 to 200 kW | 4 to 20 kW (injection molding) |
| Cost Factors | Higher initial setup, lower per-unit cost | Mold fabrication can be costly, efficient for mass production |
| Key Similarities | Both are versatile for shaping materials | Used extensively in plastics and metal industries |
Materials Used in Extrusion and Molding
| Material | Used in Extrusion | Used in Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | Widely used (e.g., PVC, HDPE) | Commonly used (e.g., PET, ABS) |
| Metals | Aluminum, steel | Less common, mainly in die casting |
| Other Materials | Composites, rubber | Silicone, various resins |
| Temperature Ranges | 350°C to 500°C (metals) | 180°C to 280°C (plastics in injection molding) |
| Key Differences | Continuous profiles | Discrete parts with complex geometries |
For more information on these processes, refer to the Wikipedia page on Manufacturing Processes.
Product Characteristics: Extruded vs. Molded
Physical Properties of Extruded Products
Extrusion is known for producing products with consistent cross-sectional profiles and specific physical characteristics.
- Material Strength: Due to the alignment of the material’s grain structure during extrusion, products often exhibit enhanced strength, especially in tensile and fatigue resistance.
- Surface Finish: Typically, extruded products have a uniform surface finish, which can vary depending on the material and extrusion process.
- Dimensional Accuracy: While extruded products are generally uniform in cross-section, they may require post-processing for precision in length and angles.
- Flexibility in Length: Extrusion allows for the production of long, continuous pieces, with length only limited by handling and transport capabilities.
Cost and Efficiency Aspects:
- Energy Requirements: Energy consumption ranges from 20 to 200 kW, influenced by material type and extrusion complexity.
- Production Cost: Initial setup costs are high, but the process is cost-effective for large volumes due to low per-unit costs.
Physical Properties of Molded Products
Molding processes are diverse, leading to a wide range of physical properties in the final products.
- Complex Geometries: Molding excels in creating complex shapes and detailed designs that are challenging or impossible to achieve with extrusion.
- Material Variety: Can handle a broader range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites, each contributing different properties to the final product.
- Surface Finish and Detail: Molded products can have a high-quality surface finish and intricate details right out of the mold.
- Dimensional Precision: Injection molding, in particular, offers high precision in dimensions, with tolerances as tight as ± 0.005 inches.
Economic and Production Considerations:
- Energy Consumption: Generally lower than extrusion, with machines consuming between 4 kW and 20 kW in injection molding.
- Cost of Production: Mold fabrication can be expensive, but efficient for mass production, leading to lower per-unit costs for large runs.
For additional information on these manufacturing techniques, the Wikipedia page on Plastic Extrusion and Injection Molding provide detailed insights.
Technological Advancements in Extrusion and Molding
Recent Innovations in Extrusion Techniques
Extrusion technology has seen significant advancements aimed at improving efficiency, product quality, and material diversity.
Co-Extrusion Developments: This technique, involving the simultaneous extrusion of multiple layers of materials, has seen improvements in precision and material compatibility, allowing for more complex and functional products.
Energy Efficiency: Modern extrusion machines are focusing on reducing energy consumption, with some new models achieving up to 20% reduction in power usage.
Smart Extrusion Systems: Integration of IoT and AI for real-time monitoring and control, leading to improved product consistency and reduced material wastage.
Material Innovations: Advances in material science have expanded the range of materials suitable for extrusion, including new composites and biodegradable plastics.
Cost and Efficiency Impact:
Production Costs: While initial investment in advanced machinery can be high, long-term savings are realized through improved energy efficiency and material utilization.
Production Speed: Newer machines offer faster speeds without compromising on product quality, thus increasing overall throughput.
Recent Innovations in Molding Techniques
Molding technologies have also undergone significant developments, enhancing versatility, precision, and environmental sustainability.
3D Printing Integration: Combining traditional molding with 3D printing to create molds rapidly and at a lower cost, particularly beneficial for prototyping and short production runs.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Increased use of sustainable and recyclable materials in molding processes, aligning with environmental conservation efforts.
Precision Molding: Innovations in mold design and material flow have led to tighter tolerances and better surface finishes in molded products.
Automation and Robotics: Advanced automation and robotics are being employed for increased precision, efficiency, and safety in molding operations.
Economic and Environmental Considerations:
Investment vs. Return: Advanced molding technologies require significant investment but offer substantial long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, product quality, and environmental impact.
Reduced Waste: Modern molding techniques focus on minimizing material waste, contributing to cost savings and environmental benefits.
These technological advancements in both extrusion and molding are setting new standards in manufacturing, with a strong focus on efficiency, quality, and sustainability. For further reading on the latest trends and innovations in these fields, the Wikipedia page on Manufacturing Technology offers a wealth of information.
