Electric cars need to be charged based on usage, typically after traveling 200-300 miles.
Factors Affecting Charging Frequency
Understanding the frequency of charging is crucial for electric vehicle owners and prospective buyers.

A. Battery Capacity
Battery capacity significantly influences the frequency of charging for electric vehicles. It’s the amount of electric energy a battery can store, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). A higher capacity means more range, reducing the need for frequent charging stops.
- High-Capacity Batteries: Vehicles with high-capacity batteries, like Tesla Model S, can travel longer distances on a single charge, reducing the number of charging instances needed.
- Low-Capacity Batteries: Conversely, electric vehicles with lower-capacity batteries may require more frequent charging.
B. Driving Habits
Aggressive driving, high speeds, and frequent stops can all lead to faster battery depletion.
- Efficient Driving: Maintaining steady speeds and avoiding sudden accelerations can extend the range, reducing the charging frequency.
- Inefficient Driving: Rapid accelerations and high-speed driving can lead to increased energy consumption and more frequent charging needs.
C. Energy Consumption
Different electric vehicles consume energy at different rates, affecting how often they need to be charged.
- Energy Efficiency: More efficient vehicles, like the Hyundai Ioniq Electric, use less energy per mile, allowing for longer intervals between charges.
- Energy Intensive Vehicles: Vehicles with higher energy consumption per mile will need to be charged more often.
Considerations
When considering an electric vehicle purchase, prospective buyers should factor in their driving habits, the vehicle’s energy consumption, and battery capacity. These factors together will give a clear picture of the charging frequency required for their specific use case. Making informed decisions can help in optimizing the use of electric vehicles and reducing the overall inconvenience related to charging.
Different Types of Charging
Understanding the types of charging is crucial for electric vehicle users as it allows them to effectively plan their journeys and manage their time. Several charging options are available, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks.
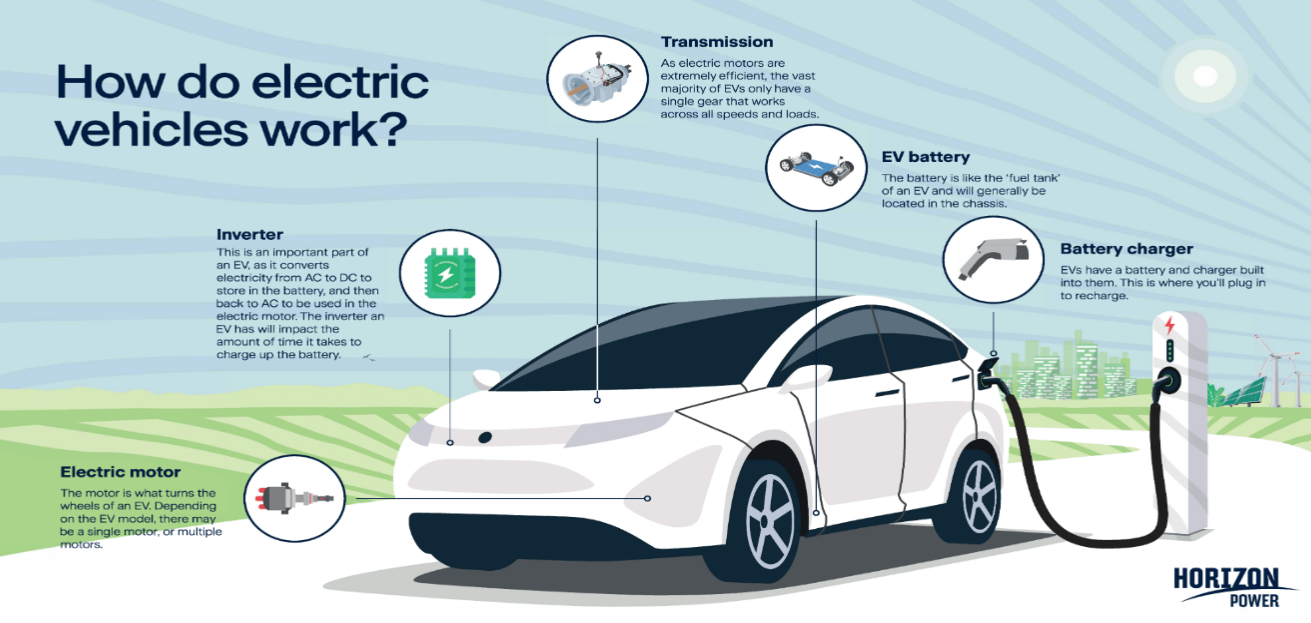
A. Overview of Charging Types
Different electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids use different types of charging options depending on the make, model, and user needs. Knowing the right type of charging for your vehicle is crucial for maximizing efficiency and convenience.
- Choosing the Right Charging Option: Selecting the appropriate charging type can help in reducing charging times and improving the overall user experience.
- Compatibility: Not all electric vehicles are compatible with every charging type, so users should consult their vehicle’s manual or manufacturer for specific information.
B. Standard Charging
Standard charging, also known as Level 1 charging, typically uses a 120V AC outlet and is the slowest charging option. It is ideal for home use and can be convenient as it doesn’t require special equipment.
- Charging Time: Standard charging can take several hours to fully charge an electric vehicle, typically providing around 4-6 miles of range per hour.
- Use Case: It’s best suited for overnight charging or for vehicles with smaller battery capacities, such as plug-in hybrids.
C. Fast Charging
Fast charging, or Level 2 charging, uses a 240V AC outlet and is commonly found in public charging stations, including those at shopping centers and parking lots. It is significantly faster compared to standard charging.
- Charging Speed: Fast charging can provide approximately 15-60 miles of range per hour, making it suitable for quick top-ups during the day.
- Accessibility: Many fast charging stations are available for public use, and some are equipped with CHAdeMO and CCS connectors to serve a variety of electric vehicles.
D. Wireless Charging
Wireless charging is a relatively new technology that allows electric vehicles to be charged without cables by using inductive charging technology.
- Convenience: Wireless charging eliminates the need for plugging and unplugging, offering a hassle-free charging experience.
- Installation: It requires the installation of a charging pad and a receiver on the vehicle, and currently, only a few models support this technology.

Implications
Knowing and understanding the different types of charging methods can aid in making informed decisions about electric vehicle usage and can significantly impact the convenience and experience of electric vehicle ownership. With advancements in technology, more efficient and user-friendly charging options are likely to emerge, enhancing the appeal of electric vehicles.
Charging Time
The charging time for electric vehicles varies widely depending on several factors. Understanding how long it takes to charge is crucial for electric vehicle owners to plan their schedules effectively and use their vehicles efficiently.
A. Charging Speed
Charging speed refers to how quickly an electric vehicle’s battery can be replenished.
- Level 1 Charging: This is the slowest charging speed, usually offering around 4-6 miles of range per hour.
- Level 2 Charging: Offers a faster charging speed, typically providing 15-60 miles of range per hour.
- DC Fast Charging: This is the fastest available, capable of adding up to 80 miles of range in just 20 minutes for some models.
B. Variables Affecting Charging Time
Several variables can affect the time it takes to charge an electric vehicle, including battery size, the state of charge, and the power output of the charger.
- Battery Size: Larger batteries will naturally take longer to charge than smaller ones.
- State of Charge: A nearly depleted battery will take longer to charge fully compared to one that’s partially charged.
- Charger Power Output: Higher power outputs will charge a vehicle more quickly, whereas lower power outputs will take more time.
C. Estimated Charging Time for Popular Models
Different electric vehicle models have varying charging times due to differences in battery sizes and accepted charging speeds. Here are some estimated charging times for popular electric vehicle models:
- Tesla Model 3: Can achieve a full charge in around 8 hours with Level 2 charging and in around 20 minutes with Supercharging, depending on the battery’s state of charge and size.
- Nissan Leaf: Takes around 8 hours to fully charge with Level 2 charging and can achieve an 80% charge in around 40 minutes with DC fast charging.
- Chevrolet Bolt: Can be fully charged in about 9 hours with Level 2 charging and can achieve approximately 90 miles of range in about 30 minutes with DC fast charging.

Conclusion
Understanding charging speeds, the variables that affect them, and the estimated charging times for different models can help electric vehicle owners make informed decisions about their vehicle usage and manage their time effectively. The choice of vehicle and charging method can significantly impact the overall user experience, so careful consideration is essential.
Charging Infrastructure
A robust and widespread charging infrastructure is pivotal for the growth and adoption of electric vehicles. The availability and accessibility of charging solutions can greatly influence the convenience and practicality of owning an electric vehicle.
A. Availability of Charging Stations
The availability of charging stations is crucial for electric vehicle users, especially for those who frequently travel long distances. The lack of sufficient charging stations can limit the usability and appeal of electric vehicles.
- Urban Areas: Generally, urban areas tend to have a higher density of charging stations, making it more convenient for city dwellers to own and charge electric vehicles.
- Rural Areas: In contrast, rural areas might have fewer available charging options, necessitating careful planning and consideration for potential electric vehicle owners.
B. Home Charging Solutions
Home charging is one of the most common and convenient ways to charge an electric vehicle, allowing owners to replenish their vehicles overnight.
- Level 1 Charging: This option is readily available to most homeowners and renters but offers slower charging speeds.
- Level 2 Charging: Requires a 240V outlet but provides faster charging speeds, making it a popular choice for home charging solutions. Installation might require professional help due to the higher voltage.
C. Public Charging Networks
Public charging networks are essential for people who do not have access to home charging and for long-distance travel. Many companies and municipalities are investing in expanding public charging networks.
- Accessibility: Highways, shopping centers, and public parking lots are common locations for public charging stations.
- Network Providers: Various providers, such as ChargePoint and Tesla Supercharger network, offer extensive networks of public charging stations with different charging speeds and connector types.
Key Considerations
When considering electric vehicle ownership, it is important to explore the available charging infrastructure in your area and along your typical routes. Assessing the availability of home charging solutions and the locations and types of public charging stations can help potential buyers determine whether an electric vehicle can suit their lifestyle and travel needs. The continuous expansion and improvement of charging infrastructure will play a significant role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles in the future.
Charging Cost
Examining the charging cost is pivotal for potential and current electric vehicle owners. It helps in understanding the economic implications of owning an electric vehicle and allows individuals to make informed decisions based on their budget and usage patterns.
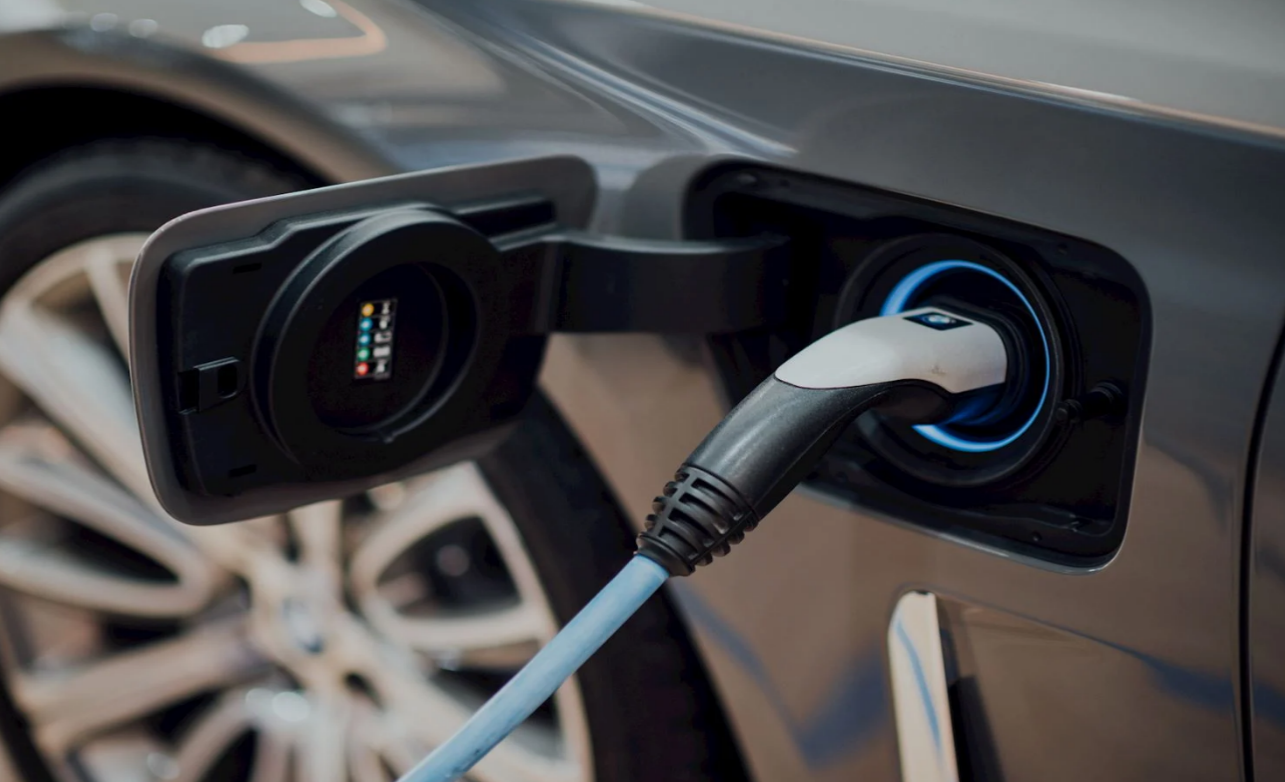

A. Electricity Prices
Electricity prices play a significant role in determining the cost of charging an electric vehicle. These prices can vary based on the location, time of day, and the electricity provider.
- Residential Charging: Charging at home is often less expensive, with the average residential electricity price being around $0.13 per kWh in the United States.
- Variable Rates: Some locations offer variable electricity rates, where the cost per kWh changes depending on the time of day, being lower during off-peak hours.
B. Charging Station Fees
Charging station fees are another component of the charging cost, especially for those who rely on public charging networks.
- Subscription Plans: Some public charging networks offer subscription plans with lower per-minute or per-kWh rates.
- Pay-as-You-Go: Many charging stations allow for pay-as-you-go payments, which may be more expensive compared to subscription plans.
C. Cost Comparison: Electric Cars vs Gasoline Cars
When comparing the running costs of electric cars to gasoline cars, it’s crucial to consider fuel efficiency, electricity, and gasoline prices. Here’s a simplified cost comparison:
| Vehicle Type | Fuel Efficiency | Fuel Cost (per gallon or kWh) | Cost per 100 miles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Car | 4 miles/kWh | $0.13 per kWh | $3.25 |
| Gasoline Car | 25 miles/gallon | $3.00 per gallon | $12.00 |
- Savings: Based on the above example, electric cars can be more economical in terms of fuel costs compared to their gasoline counterparts, leading to significant savings over time.
- Total Ownership Cost: Besides fuel costs, potential buyers should also consider other factors like maintenance costs, insurance, and depreciation to understand the total cost of ownership of electric cars compared to gasoline cars. For instance, electric cars typically have lower maintenance costs as they have fewer moving parts and don’t require oil changes, potentially making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Informed Decision-Making
By considering electricity prices, charging station fees, and making comprehensive cost comparisons, prospective buyers can understand the economic benefits and implications of owning an electric vehicle. With the continuous advancement in electric vehicle technology and the rise in gasoline prices, electric vehicles are becoming an increasingly economical choice. Potential buyers should analyze the total cost of ownership to make well-informed decisions based on their individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle.
