Yes, a transaxle can be fixed, often depending on the specific issue and the vehicle’s model.
Common Issues with Transaxles
Wear and Tear Over Time
Just like any other mechanical component, transaxles are not immune to the effects of constant use. Over time, the constant rotation and friction can lead to the degradation of internal components. Some signs of wear and tear include:
- Difficulty in shifting gears.
- Unusual noises, especially when changing gears.
- Reduced fuel efficiency.
A good preventative measure is to routinely check and replace the transaxle fluid to ensure the components remain well-lubricated.

Fluid Leaks
Fluid is crucial for the smooth operation of the transaxle. When there are leaks, it can lead to several issues:
- Inadequate lubrication, leading to increased friction and potential damage.
- Overheating due to reduced cooling capabilities.
- Visible puddles or spots under the vehicle.
Regularly checking the fluid levels and inspecting for any signs of leaks can help address this issue early on. Using a quality gasket can also prevent potential leaks.
Bearing Failures
Bearings play a critical role in reducing friction between moving parts in the transaxle. When they fail, they can cause:
- Increased friction leading to overheating.
- Difficulty in changing gears.
- A grinding or whining noise.
It’s essential to use high-quality bearings and ensure they’re adequately lubricated to prolong their lifespan.
Gear Misalignment or Damage
The gears are among the most critical components of a transaxle. When they become misaligned or damaged, it can result in:
- Difficulty in transmitting power from the engine to the wheels.
- A noticeable decrease in vehicle performance.
- Loud noises, especially during gear changes.
To prevent gear issues, always ensure that the gearbox is well-maintained and that any problems are addressed promptly.

Diagnosing Transaxle Problems
Symptoms of a Failing Transaxle
Recognizing the signs of a failing transaxle is crucial in timely intervention. Here are some symptoms to watch out for:
- Difficulty in Shifting Gears: If you’re finding it hard to shift gears or there’s a delay, it might indicate an issue with the transaxle.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, clunking, or whining noises are tell-tale signs. Often, these noises might point to issues like bearing failures or gear misalignment.
- Slipping Gears: When the vehicle unexpectedly shifts to another gear, it can be both alarming and a sign of transaxle problems.
- Fluid Leaks: Visible spots or puddles under the car, or a burnt smell, can indicate a transaxle fluid leak.
Tools and Techniques for Diagnosing Issues
To determine the exact problem with a transaxle, some specialized tools and techniques are essential:
- Diagnostic Scanners: Modern vehicles come equipped with sensors that monitor the transaxle’s performance. Diagnostic scanners can read these sensors and provide error codes which can be deciphered to pinpoint the issue.
- Fluid Inspection: Checking the quality and quantity of the transaxle fluid can reveal problems. Dark, burnt-smelling fluid indicates wear and potential damage.
- Visual Inspection: Sometimes, a simple visual inspection can identify problems like fluid leaks, damaged seals, or even external damage to the transaxle unit.
- Listening: By using a mechanic’s stethoscope or even just carefully listening, you can often identify where unusual noises originate, offering clues to the underlying issue.
- Test Drive: Taking the vehicle for a test drive and paying attention to gear shifts, noises, and overall performance can provide insights into the transaxle’s condition.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is the key to preventing minor transaxle problems from escalating into significant, expensive repairs or replacements. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Cost Savings: Addressing issues early on can save you from costlier repairs or the need for a complete transaxle replacement.
- Safety: A malfunctioning transaxle can lead to unpredictable vehicle behavior, posing a safety risk.
- Prolonged Vehicle Life: A well-maintained transaxle ensures that the vehicle runs smoothly, contributing to a longer lifespan for the entire vehicle.
- Improved Performance: A vehicle with a healthy transaxle performs optimally, offering a smoother drive and better fuel efficiency.
Can it be Repaired vs. Replaced?
When is Repair a Viable Option?
Choosing to repair a transaxle largely depends on the type and extent of the damage. Here are instances when repair might be a feasible option:
- Minor Fluid Leaks: Small leaks, often resulting from a worn gasket or seal, can generally be repaired without much hassle.
- Bearing Issues: Replacing malfunctioning bearings can restore the transaxle’s performance, especially when there’s a specific noise pinpointing to a bearing failure.
- Gear Issues: If only one or two gears are problematic, there might be an opportunity to repair or replace those specific gears without overhauling the entire system.
- Sensor Malfunctions: Modern transaxles have numerous sensors. A malfunctioning sensor can sometimes mimic a larger problem, but replacing the sensor can solve the issue.
The Pros and Cons of Repairing Versus Replacing
Deciding between repairing and replacing can be tough. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages:
Pros of Repairing:
- Cost-Effective: Generally, repairing specific components is cheaper than a full replacement.
- Less Time-Consuming: Repairs, especially minor ones, can often be completed faster than a replacement.
- Environmental Benefits: Repairing means fewer components end up in landfills, making it a more eco-friendly choice.
Cons of Repairing:
- Temporary Fix: Sometimes, a repair only serves as a short-term solution, and issues might reoccur.
- Potential for More Problems: If one component fails, others might be on their way out too. Repairing one part now might lead to more repairs soon.
Pros of Replacing:
- Longevity: A new transaxle, or a refurbished one, can extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
- Peace of Mind: With a replacement, there’s less worry about repeated issues or failures.
Cons of Replacing:
- Expensive: Replacing the entire transaxle unit can be costly.
- Time-Consuming: The replacement process might leave the vehicle out of commission for longer.
Factors that can make a Transaxle Irreparable
While many transaxle issues can be repaired, some factors can make it impractical or impossible:
- Extensive Internal Damage: If there’s widespread damage inside the transaxle, especially to multiple gears or components, repairing each one might not be viable.
- Old Age: Older transaxles might not have replacement parts readily available. Also, the wear and tear from years of use can make repair less efficient than replacement.
- Cost Prohibitive: If the cost of repairing comes close to or exceeds the cost of a new transaxle, replacement might be the more logical choice.
- Previous Repeated Repairs: A transaxle that has undergone multiple repairs might be nearing the end of its lifecycle. It might be more prone to future failures.
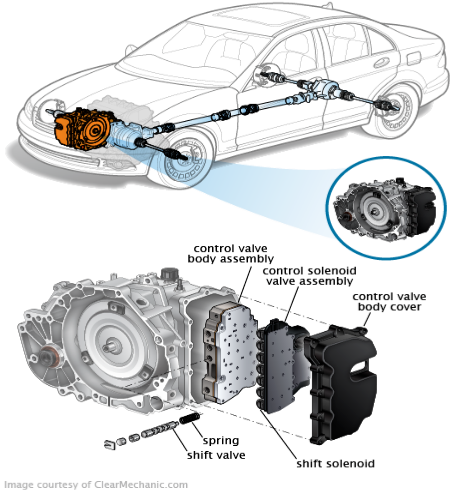
Steps to Fix Common Transaxle Issues
Draining and Replacing Transmission Fluid
Transmission fluid plays a vital role in lubricating, cooling, and cleaning the transaxle. Here’s how you can drain and replace it:
- Prepare the Vehicle: Elevate the vehicle using jack stands or a hydraulic lift for better access to the transaxle’s drain plug.
- Locate the Drain Plug: This is typically at the bottom of the transmission.
- Drain Old Fluid: Place a collection pan under the drain plug, then unscrew the plug and let the old fluid flow out.
- Replace the Filter: It’s a good practice to replace the transmission fluid filter during this process to ensure the new fluid remains uncontaminated.
- Refill with New Fluid: Using a funnel, pour the recommended type of transmission fluid into the fill port until it reaches the optimal level.
- Recheck: After refilling, start the vehicle, run it for a few minutes, then check the fluid level again to ensure it’s appropriate.
Replacing Bearings or Seals
Bearings reduce friction between the transaxle’s moving parts, and seals prevent fluid leaks. Here’s a basic guide to replace them:
- Determine the Faulty Bearing/Seal: A noisy bearing or a visible leak can help pinpoint the problem.
- Access the Transaxle: You might need to remove some components or the entire transaxle depending on the location of the faulty bearing or seal.
- Remove the Faulty Component: Carefully remove the damaged bearing or seal.
- Install the New Bearing/Seal: Ensure it’s the correct type and size, then place it in its designated spot. Lubricate bearings before installation.
- Reassemble: Once replaced, reattach any components or the transaxle itself.
Addressing Gear Issues
Gears in the transaxle can face wear, misalignment, or breakage. Addressing these issues often involves:
- Diagnose the Problem: A specific noise or difficulty in shifting can help identify which gear has an issue.
- Access the Affected Gear: This typically involves removing the transaxle and opening it up.
- Inspect and Replace: Check the gear for visible signs of wear or damage. If it’s beyond repair, replace it with a new one of the same specification.
- Test: Before sealing the transaxle, manually rotate the gears to ensure they align and function smoothly.
- Reassemble: Close the transaxle and reinstall it in the vehicle.

Fixing Minor Leaks or Cracks
Over time, the transaxle casing or its components can develop small leaks or cracks. Here’s how you can address them:
- Identify the Leak/Crack: Clean the transaxle surface and then observe to pinpoint the exact location of the leak or crack.
- Use a Sealant: For minor leaks or cracks, high-quality sealants available in auto stores can provide a temporary fix. Ensure the sealant is compatible with transaxle materials.
- Monitor: After applying the sealant, regularly check the area to ensure the leak or crack doesn’t reappear or worsen.
Preventative Maintenance
Regular Checks and Maintenance Tips
Proactive measures can significantly increase the longevity of your transaxle. Here’s a breakdown of checks and maintenance routines:
- Fluid Level and Quality: At regular intervals, check the transmission fluid level. If it appears dark or has a burnt smell, consider replacing it. A clear, reddish color indicates good fluid health.
- Inspect for Leaks: Periodically inspect the ground where the vehicle is parked for signs of leaks. If you notice any, identify the source and address it.
- Listen for Noises: While driving, pay attention to unusual noises like grinding or whining. These could indicate bearing issues or gear problems.
- Regular Service: Schedule regular services based on mileage or time intervals as recommended in the vehicle’s manual. This ensures professionals inspect and address any emerging issues.
- Temperature Monitor: Overheating can be detrimental to a transaxle. If your vehicle has a transmission temperature gauge, monitor it to ensure it remains within the recommended range.
Importance of Using the Right Lubrication
Lubrication is the lifeblood of the transaxle. Here’s why choosing the right one is crucial:
- Optimal Performance: The right lubricant ensures that the gears and components inside the transaxle move smoothly, reducing wear and tear.
- Temperature Regulation: Lubricants help dissipate heat, which is essential for the transaxle’s health. The correct lubricant will have optimal viscosity, ensuring efficient heat management.
- Corrosion Prevention: Quality lubricants also contain additives that protect the transaxle’s internals from corrosion.
- Extended Lifespan: Using the right transmission fluid or lubricant can extend the life of the transaxle by reducing the likelihood of premature wear or damage.
Keeping the Transaxle Free from Contaminants
A clean transaxle runs more efficiently. Here’s how to keep contaminants at bay:
- Regular Fluid Change: Over time, the transmission fluid can gather impurities. Regularly changing the fluid eliminates these contaminants.
- Seal Inspection: Seals prevent dirt and external contaminants from entering the transaxle. Ensure they remain in good condition.
- Filter Replacement: The transaxle’s filter captures contaminants. Replacing this filter at recommended intervals ensures optimal fluid quality.
- Clean the Exterior: Dirt and grime on the transaxle’s exterior can, over time, find their way inside. Cleaning the exterior of the transaxle during regular car washes or maintenance sessions can help prevent this.

Cost Implications
Cost of Common Repairs
While prices can vary based on location, vehicle model, and specific damage, here are some average costs for common transaxle repairs:
- Fluid Change: A standard transmission fluid change can range from $80 to $250. The price often includes both the cost of the fluid and the labor.
- Bearing Replacement: Bearings can cost between $200 and $400, but with labor, the total might come up to $500 to $900.
- Seal Replacement: A seal, while inexpensive at $20 to $50 for the part, can cost up to $200 to $500 when you factor in labor, especially if the transaxle needs to be removed.
- Gear Repair: Addressing gear issues can be pricier. Individual gears might cost $100 to $500, but labor-intensive repairs can push total costs up to $1,000 to $3,000.
Factors Affecting Repair Costs
Various elements influence the final repair bill:
- Vehicle Make and Model: Luxury or rare vehicles might have pricier parts and specialized labor requirements.
- Extent of Damage: Minor issues will generally be cheaper to address than severe damage requiring multiple repairs.
- Labor Costs: Rates can vary based on the mechanic’s experience, location, and the complexity of the job.
- Part Availability: Readily available parts are usually cheaper than those that need to be special-ordered or are rare.
- Location: Repairing a transaxle in urban areas or regions with a high cost of living might be more expensive than in other areas.
Comparing Costs: Repair vs. Replacement
When faced with a transaxle issue, one of the pivotal decisions is whether to repair or replace:
- Repair: As outlined above, individual repairs can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the issue. Multiple repairs might make this option less economically viable in the long run.
- Replacement: A new transaxle can cost anywhere from $1,500 to $3,500 for standard vehicles, and up to $10,000 for luxury or specialized cars. Add in labor, and you’re looking at a total of $2,500 to $5,000 for most cars. While this might seem steep, it’s often a more cost-effective solution if the existing transaxle has multiple issues or is nearing the end of its lifespan.
In many cases, consulting with a trusted mechanic can help in making an informed decision. It’s essential to consider both the immediate financial implications and the potential long-term costs associated with each option.
